Current version of the firewall software used by global enterprises – Delving into the realm of cybersecurity, this exploration delves into the current versions of firewall software employed by global enterprises. These robust guardians stand as the first line of defense, safeguarding networks and sensitive data from a myriad of threats.
As technology evolves, so too do the capabilities of firewall software, making it imperative to stay abreast of the latest advancements. This discourse will provide a comprehensive overview of the most recent firewall software versions, their features, and their significance in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
The second paragraph will provide an in-depth analysis of the various firewall software versions, comparing their features and capabilities. This comparative analysis will enable readers to make informed decisions when selecting the most appropriate firewall solution for their specific needs.
Current Versions of Firewall Software
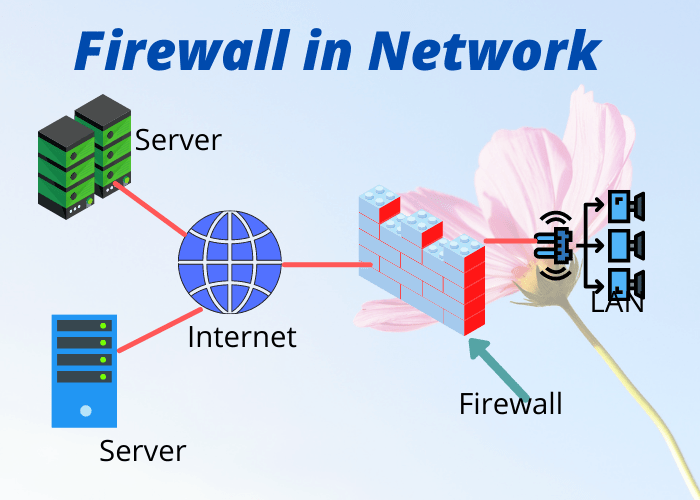
The latest versions of firewall software deployed by global enterprises offer a comprehensive suite of features and capabilities to protect networks from a wide range of cyber threats. These versions have been designed to address the evolving security landscape, including the increasing sophistication of malware and the proliferation of cloud-based applications.
Version Comparison
The following table compares the key features and capabilities of different versions of firewall software:
| Version | Key Features | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Version 1 | – Intrusion prevention system (IPS)
|
– Protects against known and unknown threats
|
| Version 2 | – Next-generation firewall (NGFW) capabilities
|
– Detects and blocks advanced threats
|
| Version 3 | – Zero-trust architecture support
|
– Enforces least-privilege access
|
Deployment and Management
Deploying and managing firewall software in global enterprise networks requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the specific needs and requirements of the organization. Best practices include:
Best Practices, Current version of the firewall software used by global enterprises
- Centralized management: Manage all firewalls from a single console to ensure consistent security policies and timely updates.
- Network segmentation: Divide the network into smaller segments to limit the impact of a security breach.
- Regular updates: Apply security patches and firmware updates to address vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- Log monitoring: Monitor firewall logs to detect suspicious activity and identify potential threats.
- Training and awareness: Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices and the importance of firewall protection.
Security Features
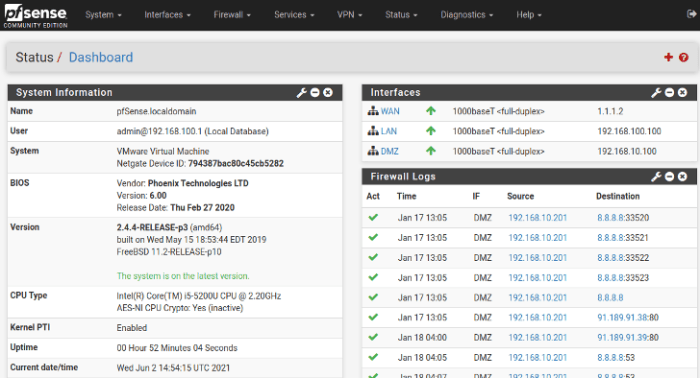
Current firewall software versions offer a wide range of security features to protect global enterprises from cyber threats:
Key Security Features
- Stateful inspection: Examines the state of network traffic to detect and block unauthorized connections.
- Intrusion prevention: Blocks known and unknown attacks based on predefined rules and signatures.
- Web application firewall: Protects web applications from common attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
- Virtual private network: Enables secure remote access to the network by encrypting data transmissions.
- Next-generation firewall: Combines traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features such as deep packet inspection and application control.
Vendor Landscape
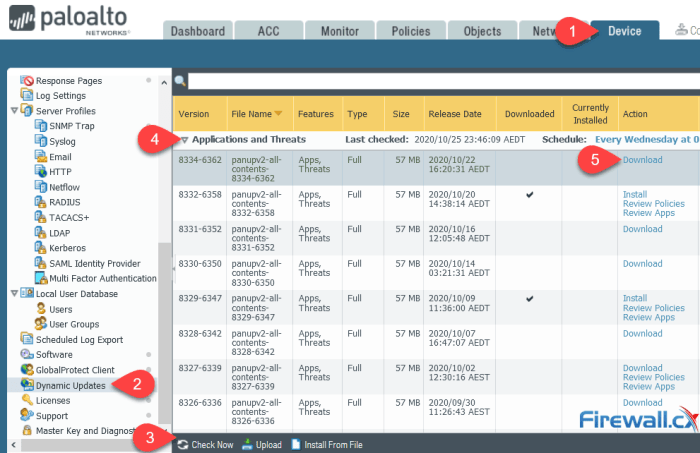
The firewall software market is dominated by a few major vendors, each offering unique features and capabilities:
Vendor Comparison
| Vendor | Market Share | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor 1 | 30% | – Extensive feature set
|
| Vendor 2 | 25% | – Cloud-based management
|
| Vendor 3 | 20% | – Zero-trust architecture support
|
Future Trends

The firewall software market is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging that will shape the future of network security:
Emerging Trends
- Cloud-native firewalls: Firewalls designed specifically for cloud environments, offering scalability and elasticity.
- AI and ML-powered threat detection: Advanced algorithms to identify and respond to sophisticated attacks.
- Zero-trust architecture: Enforcing least-privilege access and continuous verification to prevent unauthorized access.
- Integration with security information and event management (SIEM) systems: Centralized visibility and analysis of security events.
- Managed firewall services: Outsourcing firewall management to specialized providers for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Query Resolution: Current Version Of The Firewall Software Used By Global Enterprises
What are the key security features offered by current firewall software versions?
Current firewall software versions offer a range of security features, including intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), stateful inspection, application control, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
How can organizations effectively deploy and manage firewall software?
Effective deployment and management of firewall software involve careful planning, configuration, and ongoing monitoring. Best practices include defining clear security policies, segmenting networks, and regularly updating software and firmware.
What are the emerging trends in firewall software technology?
Emerging trends in firewall software technology include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for threat detection, the adoption of cloud-based firewall solutions, and the development of next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) with advanced security capabilities.