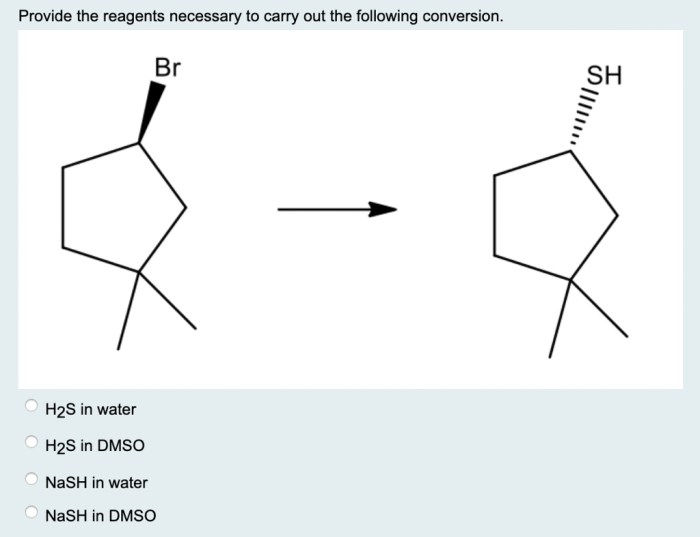
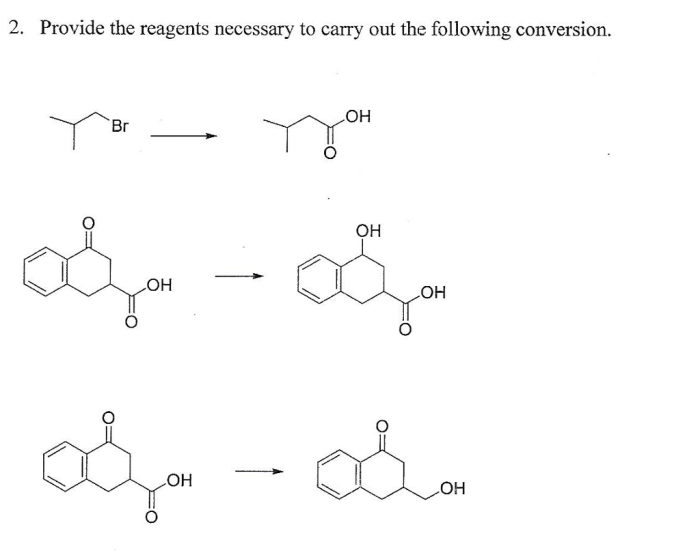
Provide the reagents necessary for the following conversion – In the realm of chemistry, reagents play a pivotal role in facilitating chemical reactions. This article delves into the concept of reagents and their significance, providing a comprehensive guide to identifying, selecting, preparing, and handling reagents effectively. By understanding the principles and applications of reagents, chemists can optimize chemical conversions and achieve desired outcomes.
Reagents are substances that participate in chemical reactions, providing the necessary elements or functional groups to drive the transformation of reactants into products. Their selection and use are crucial for successful chemical synthesis and various industrial processes.
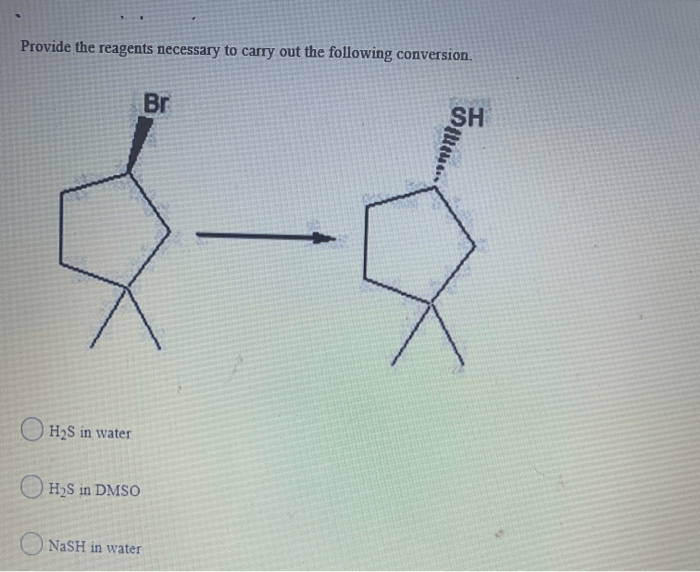
Reagents for Chemical Conversions: Provide The Reagents Necessary For The Following Conversion
Reagents are essential substances that facilitate chemical reactions. They provide the necessary elements or functional groups to drive the desired transformation.
Methods for Identifying Required Reagents, Provide the reagents necessary for the following conversion
- Chemical Equations: Analyze balanced chemical equations to determine the reactants and products.
- Reaction Mechanisms: Understand the step-by-step mechanism of a reaction to identify the intermediates and catalysts.
- Databases and Literature: Consult scientific databases and literature to search for known reagents for specific conversions.
Factors Influencing Reagent Selection
- Cost and Availability: Consider the economic feasibility and accessibility of the reagents.
- Reactivity: Choose reagents that react efficiently under the desired conditions.
- Purity: High-purity reagents minimize side reactions and ensure accurate results.
- Reaction Conditions: Temperature, solvent, and other reaction parameters can affect reagent selection.
Reagent Preparation and Handling
- Safety Precautions: Handle reagents with appropriate protective gear and follow safety protocols.
- Storage and Disposal: Store reagents according to their specific requirements and dispose of them properly.
- Specialized Equipment: Use specialized equipment such as glove boxes or vacuum lines for handling sensitive reagents.
Examples of Reagent Use in Chemical Conversions
- Acid-Base Reactions: Acids and bases react to form salts.
- Redox Reactions: Oxidizing and reducing agents facilitate electron transfer.
- Organic Synthesis: Reagents like Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds are used in complex organic transformations.
Troubleshooting Reagent-Related Issues
- Reagent Contamination: Identify and remove contaminants to ensure reaction accuracy.
- Reagent Degradation: Monitor reagent stability and replace degraded reagents as needed.
- Reaction Optimization: Adjust reagent ratios and reaction conditions to improve efficiency and yield.
Commonly Asked Questions
What factors influence reagent selection?
Factors influencing reagent selection include cost, availability, reactivity, purity, and the impact of reaction conditions (e.g., temperature, solvent).
How can I identify the reagents required for a specific conversion?
Various methods can be used, such as analyzing chemical equations, reaction mechanisms, databases, and literature.
What are the common problems that can arise during reagent use?
Common problems include reagent contamination, degradation, and improper storage, which can impact reaction outcomes.