Embark on a scientific expedition with our karyotyping activity answer key PDF, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the secrets of chromosomal analysis. This invaluable resource empowers you to decipher the complexities of karyotypes, unravel genetic mysteries, and gain a deeper understanding of human health and inheritance.
Through a meticulous exploration of karyotyping basics, procedures, interpretation, and applications, this answer key illuminates the intricate world of chromosomes, empowering you to make informed decisions and advance your knowledge in the field of genetics.
1. Karyotyping Basics
Karyotyping is a laboratory technique that involves the analysis of an individual’s chromosomes. Chromosomes are structures within cells that carry genetic information. Karyotyping provides a visual representation of an individual’s chromosomal makeup, allowing for the identification of any abnormalities that may be present.
Karyotyping is commonly used in genetic counseling to identify individuals at risk for genetic disorders. It can also be used to diagnose genetic disorders, monitor treatment, and study the effects of environmental toxins on chromosomes.
Types of Karyotyping Methods
- Standard karyotyping:This method involves culturing cells in the laboratory and staining them with a dye that makes the chromosomes visible under a microscope.
- Spectral karyotyping (SKY):This method uses fluorescent probes to paint each chromosome with a different color, making it easier to identify individual chromosomes and detect abnormalities.
- Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH):This method compares the DNA of an individual to a reference genome to identify any regions of loss or gain.
- Microarray-based karyotyping:This method uses DNA probes to identify and quantify specific chromosomal regions, allowing for the detection of smaller abnormalities than traditional karyotyping.
2. Karyotyping Procedure: Karyotyping Activity Answer Key Pdf
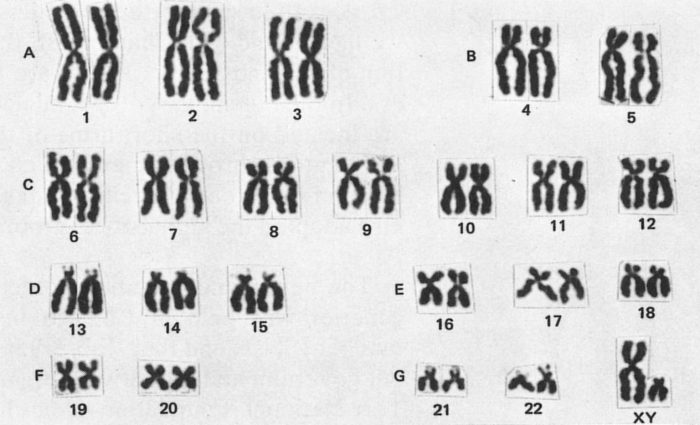
The karyotyping procedure involves several steps:
- Cell culture:Cells are collected from the individual and cultured in the laboratory to allow them to divide and multiply.
- Chromosome preparation:The cells are treated with a chemical that causes them to swell and burst, releasing the chromosomes.
- Staining:The chromosomes are stained with a dye that makes them visible under a microscope.
- Analysis:The stained chromosomes are arranged in a karyotype, which is a visual representation of the individual’s chromosomal makeup.
The karyotype is then analyzed to identify any abnormalities, such as missing or extra chromosomes, or structural rearrangements.
3. Karyotyping Interpretation
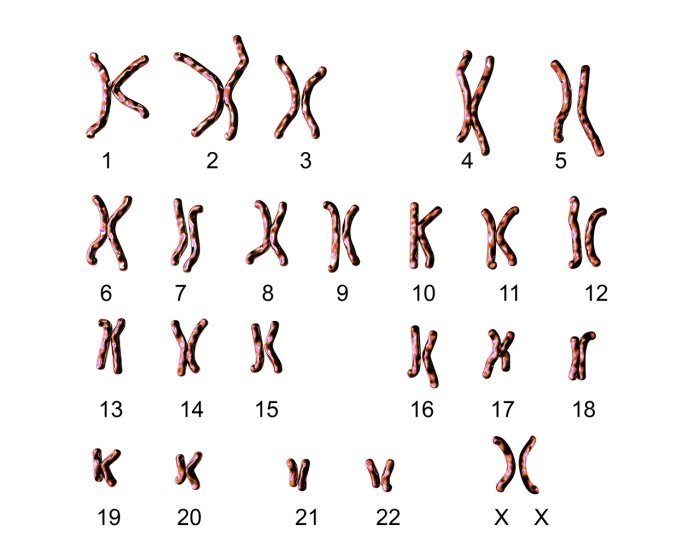
Karyotype interpretation involves the analysis of the chromosomal makeup of an individual to identify any abnormalities. Chromosomal abnormalities can be classified into two main types:
- Numerical abnormalities:These involve changes in the number of chromosomes, such as missing or extra chromosomes.
- Structural abnormalities:These involve changes in the structure of chromosomes, such as deletions, duplications, or inversions.
Karyotyping can be used to diagnose a wide range of genetic disorders, including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome.
4. Karyotyping Applications
Karyotyping has a wide range of applications in various fields:
Prenatal diagnosis, Karyotyping activity answer key pdf
Karyotyping can be used to identify chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus during pregnancy. This information can be used to counsel parents about the potential risks and outcomes of the pregnancy.
Cancer research
Karyotyping is used to identify chromosomal abnormalities in cancer cells. This information can help to determine the type of cancer, predict its behavior, and guide treatment decisions.
Forensic science
Karyotyping is used to identify individuals from DNA samples. This information can be used to solve crimes and identify missing persons.
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of karyotyping?
Karyotyping is a laboratory technique used to analyze the number and structure of chromosomes in an individual’s cells. It is primarily used to identify chromosomal abnormalities that may be associated with genetic disorders or developmental issues.
How is karyotyping performed?
Karyotyping involves several steps, including cell culture, chromosome preparation, and staining. Cells are collected from the individual and cultured in a laboratory setting to stimulate cell division. The chromosomes are then extracted from the cells and stained to make them visible under a microscope.
What types of chromosomal abnormalities can be detected through karyotyping?
Karyotyping can detect various chromosomal abnormalities, including numerical abnormalities (such as aneuploidy, where there is an abnormal number of chromosomes) and structural abnormalities (such as deletions, duplications, or translocations, where there is a change in the structure of chromosomes).